Written by Jackie Armstrong
When I took my first steps into the world of visitor research and evaluation there was a lot of emphasis on how to make the museum a more engaging place. The word engaging often got thrown around with no outline of what that actually looked in practice, or sometimes even no explanation as to why an engaging experience was what a museum should be trying to achieve. Engaging for whom, in what ways, and under what circumstances? Everyone used the word but the nuances were very different depending on the person and the situation. This was something I was hyperconscious of and always tried to address in my evaluation practices.
I’m noticing a very similar thing happening now with how the word trauma is used, in particular as more institutions and organizations talk about being trauma aware, trauma sensitive and/or trauma informed. I’m thrilled there is finally more focus on the prevalence and impact of trauma, but I am aware that not everyone is talking about the same thing or on the same page and also recognize how far we have to go in realizing a trauma informed museum. This is something I’ve been wanting to address, professionally as someone who advocates for visitors through evaluation and research and as a person engaged in intensive trauma therapy and working on healing from the impact of traumas in my life.
It is my firm belief that museums have a responsibility to do the work to become more trauma informed, not later but now. Museums are not standalone containers for housing art, but hubs of human interaction located within communities. If museums wish to be truly relevant to people and be spaces in which people can safely and purposefully come together to experience art in layered and meaningful ways, and be able to show up as their authentic selves, then museums must become trauma informed. This requires a culture change throughout the museum, not just using trauma informed practices in one department within the museum. This is something I’ve felt urgency around for quite awhile but feel that both COVID-19 and the issues underlying the Black Lives Matter movement are bringing all of this into focus even more as collectively our worldviews have collapsed and individually we are all dealing with survival reactions. A growing sense of unease has flooded our consciousness, many of us pushing for changes that require solidarity, intentionality, and unwavering action.
“Traumatic experiences and oppressive social conditions cause us to move into a series of automatic, holistic, and incredibly creative means of first surviving then adapting to the harm, ruptured connection with ourselves and others, and betrayal. We are built for safety, belonging, and dignity. We are built to be connected to and make a difference for others, to have meaningful lives. When any of these core needs are disrupted through trauma, we automatically attempt to protect ourselves….Traumatic experiences are always happening within a social context and shaped by social conditions. They are nearly always perpetuating the “rules of engagement” of our social conditions.” (Staci K. Haines, Somatics, Healing, and Social Justice: The Politics of Trauma, Chapter 4)
Let’s think about COVID-19 first. To start, we have this invisible threat that no one fully understands but it’s clear that some people get very sick and even die. It spreads easily and rapidly and we can get it just by going about our lives. We fear getting sick and potentially dying and we fear loved ones getting sick and dying, and in order to keep each other safe we need to stay away from one another, which goes against our instincts as humans. We are asked to isolate in our living environments and practice physical distancing. We develop rituals around cleanliness and hygiene in an effort to thwart the virus and we scan news sources constantly hoping for answers. Levels of hypervigilance are at an all time high for many. And while we do these things, we are given mixed information from those in power that only adds to the emotional dysregulation we’re experiencing. Dysregulation makes it difficult to manage and recover from the intense emotions that might come from upsetting situations. Prolonged emotional reactions take a toll on our physical and mental well-being. There are several results from all of this: feelings of powerlessness, a deep sense of dread for the future, overreactions to “little things”, a near constant state of fear, mood swings, sleeplessness, and more.
Added to the constant threat to life that COVID-19 leaves many people with is the economic instability that comes with lockdown, the loss of regular coping strategies, and perhaps worse, the inability to have physical contact with people in your life who you would normally turn to for comfort. It’s an extremely disorienting time. Our bodies, to varying degrees, live out the state of emergency we are in and our bodies fight the isolation that we must endure to keep one another safe. For those with existing unresolved trauma, everything surrounding COVID-19 escalates these experiences. None of us can orient to the threat of COVID-19 because we cannot see it, nor can we adequately flee it or fight it, so a lot of our reactions become internalized or come out in other ways such as the dysregulated emotional responses mentioned above, as well as physical symptoms such as migraines, gastrointestinal issues, inflammation and other physical pain.
Early into the COVID-19 outbreaks in the United States, the glaring inequality that has existed for so long came into focus for many more people as BIPOC are impacted by COVID-19 more than white people and also face unemployment at higher rates. Along with this there has been a surge in police brutality against Black people, something that has been going on for far too long, and perhaps because of COVID-19 more people, specifically white people, finally are taking notice of the massive injustices and inhumanities taking place. The present moment is asking everyone to not look away or remain silent but to rise together and fight these injustices. All of this against a backdrop of climate change and political instability.
There is a pervasive weight of fear and grief everywhere. The world is literally screaming for us to heal. Something must shift.
Before we talk about what a trauma informed museum is and what that might look like in practice it’s important to start by considering what trauma is.
What is Trauma?
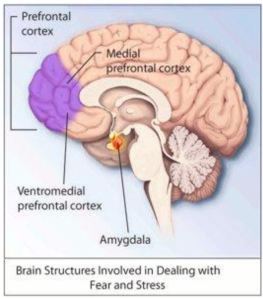
The first thing to know about trauma is that it exists on a spectrum. When people talk about trauma they often refer to a specific event or series of circumstances but trauma is actually more about how the brain and body processes those experiences. Everyone experiences trauma at some point in their life and everyone to some degree has unintegrated traumatic experiences. Unintegrated trauma is that which hasn’t been properly acknowledged or contextualized and therefore remains trapped in the body, instead of being processed and moved through. When trauma isn’t integrated into someone’s consciousness and/or when the natural reaction to trauma hasn’t been given space to be felt (e.g. feeling anger, grief, being able to escape), it gets stuck. This is problematic for many reasons but mostly because it impacts the present, causing reactions that are out of place and out of proportion to things happening in the current time or situation. This is why trauma treatment often involves modalities outside of talk therapy, for example EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) and/or SE (Somatic Experiencing). There are many different types of trauma or large categories of experiences that can result in trauma such as early childhood trauma, cumulative trauma, interpersonal trauma, developmental and attachment trauma, trauma in adulthood (often, but not always, re-enactments of early trauma), systemic injustice, intergenerational trauma, racial trauma, immigration trauma and many more. The list of symptoms that can be associated with trauma is lengthy and goes far beyond the flashbacks and nightmares mostly commonly thought of, having repercussions on the brain and body.
Most people cannot begin to process trauma, and therefore heal from it, until they feel safe. Safety and stability are critical. People who have someone who is able to co-regulate and be with them, at the time trauma occurs, can often move through the experience more quickly so that the trauma doesn’t have as long lasting or as severe of an impact as it does for someone who has no one to be with them in their pain. This is one reason why childhood trauma can continue to haunt people into adulthood as most people at the time their childhood trauma occurred did not have adequate support in place, in particular if their caregivers were the abusers. At the heart of trauma is a sense of isolation, disconnection and feeling of not belonging. Trauma asks to be seen, heard and felt and therefore requires connection and community. Healing from trauma involves the relief of suffering, validation for what has been endured, and words and action which seek to make sense out of something which defies reason. Everyone’s individual nervous systems as well as access to resources (external but also internal) plays a big role in one’s ability to heal.
Trauma is about overwhelm. It’s about something happening that is too much, too fast, or too soon for the body and mind to take in. Trauma is about unmetabolized information that gets stuck in the body and makes it hard for people to heal from. Trauma is about the nervous system, intolerable sensations and emotional dysregulation. Trauma is about dissociation as an unconscious survival mechanism. Trauma is about defense mechanisms and shame responses. Trauma is about activation levels and hypervigilance. Trauma is about not feeling safe in one’s own body and feeling disconnected from the world. Trauma is about the impact on a person’s life, which can be enormous, layered and long lasting, but it is also about hope, resilience and finding your way home, both to yourself and to a community of supporters.
One of the clearest definitions of trauma comes from Howell (2020) who explains that:
“trauma is that which causes dissociation, that is, it causes a blank spot, or fissure in experience, causing a deficit in the ability to regulate affect and to make sense of things. This conceptualization has the advantage of bypassing debates about the meaning of objectively defined trauma (which does not result in post-traumatic stress to all those exposed to it) and subjective trauma (which can run the risk of categorizing anything that is distressing as traumatic)…. An experience is traumatic if it is overwhelming enough to cause a break in the linkage and meaning of experience, in narrative memory, and even in body processing. When an event cannot be assimilated into the rest of the experiencing self, it becomes, as Pierre Janet so well described a fixed idea that is isolated and disconnected from the rest of the self.” (Howell, pp.30-31, 2020)
Why is it important that art museums understand trauma and implement trauma informed guidelines, practices and processes?
The simple answer is because art museums are places where people come together, people with diverse life experiences, perspectives, interests, abilities, learning styles, identities AND traumas. Art museums are spaces where many nervous systems come together, in various levels of activation, navigating a dense landscape of art and sensory inputs. And ideally art museums are much more than a building where art is put on view, but places where people are invited to show up as their authentic selves and enter into dialogue with the art, one another and with themselves internally. Art has long been an outlet to communicate when words fail or are simply not enough. A great deal of art has been born out of traumatic experiences, seeking to process and give voice to what is not easily put into words. When art is created and viewed, it breaks through the isolation under which it might have been created and opens up the door to healing. Art connects with people in emotional and visceral ways, sometimes stirring something in us that we have yet to explore or perhaps even triggering past or current trauma. Art can connect to parts of the unconscious, open our eyes to our own truths, speak to our own suffering and offer new perspectives. Art always connects to place and time, echoing something back from the moment it was created. Art is never silent. Viewing art, particularly in the communal space of the museum, can be just as much a part of the healing process as its creation might be for the artist.
Large art institutions often welcome people from around the world and their doorsteps, both onsite and online. These museums have a responsibility to acknowledge the present moment and the life events collectively witnessed and/or experienced. It’s just as important for staff at museums to have space and time to come together and connect with one another as it is for the museums to connect to their audiences in meaningful and diverse ways. Museums must be responsive to the times we live in and the ever-changing needs of audiences (those who come through the doors and those who don’t), listening rather than making assumptions about those needs.
In many cases, art museums onsite visitorship does not reflect the racial and economic diversity of the locations they are situated in, this is particularly true of those located in densely populated cities, however they are often able to reach a more diverse audience online. MoMA, for example, has an expansive reach online, that has continued to grow during the coronavirus pandemic, and is reaching new audiences. For many people, engaging with a museum online is more accessible than an in-person visit and/or marks the first step in greater engagement with the institution (perhaps eventually leading to an onsite visit). The trauma-informed art museum does not serve “only” a few people, it considers the well-being of the whole and creates spaces and opportunities for healing, connecting, creating, feeling, learning, sharing and transforming in ways that gently support individual inclinations. A trauma informed art museum does more than acknowledge trauma, it recognizes it, works to connect people to a shared humanity and fosters cultural humbleness, refrains from othering, avoids retraumatization and puts the physical, emotional and mental well-being of people above all else.
A trauma-informed art museum considers and asks:
- By accepting that everyone has trauma and that some people are impacted more severely by it, what can we do to contribute to the conditions of healing and recovery? How can the museum be part of the healing process, thinking creatively, transparently and inclusively about this?
- How can we help to understand the impact of trauma on our visitors and colleagues and how trauma experiences might manifest so that we are better able to be understanding, supportive and nimble enough to meet people where they are? How might we consider trauma in our planning and programming efforts to ensure we are inclusive and accessible?
- People with trauma disorders often face stigma from the lack of information and/or from misinformation, especially when they have additional mental health diagnoses. Growing our own awareness can help break down some of this stigma. What are some steps we can take to break down stigma, individually and collectively? How might we better support people facing stigma and why is it important to do so?
- The grounding skills, coping strategies and somatic exercises often used in treating people with trauma disorders are helpful to anyone who experiences trauma in their lifetime. If we all learn these skills we can better self-regulate and also help co-regulate those who may be struggling, whether a colleague or a visitor. Over time these efforts can increase our emotional capacities which reduces personal suffering and also frees us up to help others.
What does all this look like in practice?
There are many guidelines to trauma informed principles, some organizations (in healthcare, education, the arts etc.) tailoring the principles to their individual missions but all of them at their core seek to do no harm by establishing a culture that promotes healing. Of all the trauma informed guiding principles I’ve read to date, the ones outlined by Nkem Ndefo, creator of the Resilience Toolkit, resonates with me the most and seems most appropriate for a public institution such as a museum. As Nkem Ndefo explains, these trauma informed guidelines are principles for living a humane life. These 6 principles include: “1) Safety 2) Trust and Transparency 3) Collaboration and Mutuality 4) Peer Support 5) Voice, Choice, Self Agency 6) Cultural Humility.” When you think about a museum and all of the people who are impacted by it, visitors and staff, these guidelines make perfect sense.
It’s worth noting at this point that over a year ago the Education Department at MoMA went through several workshops to update our core values and collectively landed on the following as being key to the work we do: 1) Empowerment – honor people’s experiences. Share power. 2) Empathy – Build relationships. Foster Understanding. 3) Radicality – Challenge norms. 4) Embrace questioning. Think anew. 5) Creativity – Take risks. Value imagination and experimentation 6) Joy – Work with presence, passion and authenticity. These core values could complement trauma informed practices if considered through that lens.
Trauma informed practices prioritize people, in the case of a museum this includes visitors AND staff. Creating safe spaces, fostering empowerment and actively listening are a big part of this, as well as recognizing the intersectionality that exists in all of our lives. When thinking about programming, meetings, and other experiences at the museum trauma informed guidelines might look something like this:
- Create moments of calm and establish practices that promote groundedness, tolerance (of sensations, differing perspectives), presence (in the moment), intentionality, and radical acceptance, using art as a jumping off point and/or as inspiration
- Offer a range of activities and prompts that increase a sense of connectedness to self and others, focusing on themes of community, collaboration and internal peace
- Help grow empathy and compassion for self and others using a range of modalities, particularly reflection and visualization
- Share skills/tools/coping mechanisms for dealing with stress, uncertainty, and intense emotions or reactions through practices and activities that encourage self-awareness and attunement
- Offer activities, suggestions, and experiences which help people be in the moment and grow their individual resilience and capacity for managing difficult circumstances, emotions, or thoughts
- Facilitate exchange which validates personal and collective experiences, allowing individuals to create meaning using their own life narratives while opening the door to new perspectives and different narratives, strengthening their understanding and compassion for themselves and others as well
- Encourage people to respect where they are, and where others are, in any given moment (to check-in with themselves) and to enter into new experience with curiosity
Some of this involves shifts in our language, experimenting with new program formats, the pacing of programs and how we collaborate with one another (including working with new people and fresh ideas), but it’s also about flexibility, being aware of our own nervous systems and how they interact with others, regulating our emotions, modelling and mirroring embodied presence and awareness, and perhaps most importantly creating and holding space for one another.
This is NOT about museum staff being therapists or doing work that they do not have expertise in, this is asking that the museum operate in a more humane and holistic manner so that all staff feel encouraged to contribute to these efforts. Within the context of a program, trauma informed practices can feel therapeutic but they are not a substitute for a therapy program.
Why does it matter?
Trauma informed practices and principles acknowledge humanity and are beneficial to all, including those with acute trauma disorders, people who have experienced trauma in the past but have moved through it and everyone in between. Universal Design principles for multi-modal engagement is something that museum education has championed for years, because it benefits everyone, not just people with disabilities. Trauma informed practices similarly have universal benefits.
Systemic change cannot happen unless people feel safe, and in order to effect transformative cultural change trauma informed principles must be adopted museum-wide and used as a guide. Using trauma informed practices in one department, while significant, will not have as big an impact as a museum where trauma informed principles are taken up museum-wide. For example, a small group of us in the Education Department at MoMA have started an initiative called Artful Practices for Well-Being and have been meeting since May to discuss experiences with art through the lens of trauma-informed practices. The conversations and efforts have been encouraging but they are not enough.
Museums are spaces where individual and collective narratives make contact, whether that’s the art and the stories attached to works, audiences that visit onsite or online, or the staff who work there. Trauma is present within some of those narratives, which might rise to the surface through the interactions at a museum, and those should not be ignored or silenced. Trauma informed practices acknowledge the traumas that filter into museum spaces, rather than setting them aside or avoiding them. Museums can and should be safe-enough places, as Ross Laird outlines, where emotions can be felt and traumas can be held, where people are invited to reflect, share their thoughts and offered choices in how they move through and engage with the museum, and feel supported in personally meaningful exploration.
In my understanding and imagining of what a trauma informed art museum could be, I always think about it as a nurturing environment, one where the experience of everyone is thoughtfully considered and the people who visit and work there are recognized for all that they bring with them, including the weight of trauma. A trauma informed art museum experience ensures that we all have space and resources to make meaning, connect and heal, as individuals and in community with one another. Museums should be places where everyone who wishes to be there feels a sense of belonging and feels called upon and empowered to show up as their best selves, but where the practices and principles in place help to regulate our nervous systems when we are not feeling our best. A trauma informed art museum unites us in our shared humanity but validates and makes space for the individual truths and lived experiences we all carry.
Here’s a quote I keep coming back to that I hope you will find inspiration in as well:
“What would it look like to belong in the world as our whole selves? What kinds of culture, knowledge and community structures would we be able to create if we could nurture one another without our armor on, if we could draw out and develop the gits in one another, if we could care for another in concrete, meaningful ways, and could protect one another from systemic harms and forms of structural violence, even as we’re struggling to dismantle them? What do we already have waiting within us that can guide us in that direction?” (Nora Samaran, p.14, Turn This World Inside Out: The Emergence of Nurturance Culture)
About the Author
JACKIE ARMSTRONG is the Associate Educator, Visitor Research and Experience at The Museum of Modern Art where she works cross-departmentally planning, coordinating, conducting and sharing the results of visitor research and evaluation, as well as working on other initiatives and interpretive resources. She leads Audiences Advocates, a cross-departmental group that uses agile evaluation to inform the design process, specifically of digital resources. Most recently, Jackie has been busy co-leading Artful Practices for Well-Being, a new initiative stemming from her passion for considering trauma informed practices in museum work. Previously, she served as the Audience Researcher in the Education Department at the Art Gallery of Ontario. She completed an MA in Museum Studies at the University of Toronto and has completed studies in Classics: Ancient Art and Archaeology, Anthropology, and Tourism Management Systems. Jackie is interested in the ways in which museums can connect with diverse publics, create thoughtfully designed experiences, and empower people to make personal meaning through their encounters with art, one another and their personal life histories. As an advocate for visitors she believes strongly in using evaluation methods to help museums make informed decisions for improving the visitor experience and taking the time to really listen to people. Jackie has presented at MCN, VSA, AAM and NYCMER, as well as written for several museum publications.
Increasingly, Jackie is drawing on her personal experiences with trauma and mental health as she works on healing, using her insights, knowledge and research to advocate for others and inform her work in the museum. Jackie is a regular contributor to The Mighty and is looking forward to doing more advocacy work in the future as she moves along in her own recovery. When not working on visitor research, writing or reading, you can find Jackie engaged in therapy, trying out new ice cream flavors, painting, spending quality time with friends, exploring NYC and watching past episodes of Survivor.
Jackie’s postings on this site are her own and don’t represent the Museum of Modern Art’s positions, strategies, or opinions.
Works Cited:
Haines, Staci K. (2019). Somatucs, Healing, and Social Justice: The Politics of Trauma. Berkeley, California. North Atlantic Books.
Howell, Elizabeth. (2020). Trauma and Dissociation Informed Psychotherapy; Relational Healing and the Therapeutic Connection. New York, New York. W. W. Norton and Company.
Laird, Ross. (2020). Mental Health Considerations for Museums: An Emerging Field of Practice and Discovery. Adapted from Museum Objects, Health and Healing, by Brenda Cowan, Ross Laird,, and Jason McKeown.
Ndefo, Nkem. (2020). Nkem Ndefo on Trauma and Resilience (#113). CHITHEADS from Embodied Philosophy (Podcast). New York, New York.
Samaran, Nora. (2019) Turn This World Inside Out: The Emergence of Nurtance Culture. Chico, Edinburgh. AK Press.
Other Works that Have Informed Thinking:
Chefetz, Richard A. 2015. Intensive Psychotherapy for Persistent Dissociative Processes: The Fear of Feeling Real. New York, New York. W. W. Norton and Company.
Dixon, Ejeris, and Leah Lakshmi Piepzna-Samarasinha, Editors. (2020). Beyond Survival: Strategies and Stories from the Transformative Justice Movement. Edinburgh, Scotland. AK Press.
Evans, Amanda, and Patricia Coccoma. (2017). Trauma-informed Care: How Neuroscience Influences Practice. New York, New York. Routledge.
Fisher, Janina. (2017). Healing the Fragmented Selves of Trauma Survivors: Overcoming Internal Self-Alienation. New York, New York. Routledge.
Foreigner, Christine C. (2017). Dissociation, Mindfulness, and Creative Meditations: Trauma-informed Practices to Facilitate Growth. New York, New York. Routledge.
Goulding, Regina A. and Richard Schwartz. 1995. The Mosaic Mind: Empowering the Tormented Selves of Child Abuse Survivors. New York. New York. W. W. Norton and Company.
Herman, Judith. 1992. Trauma and Recovery: The Aftermath of Violence – From Domestic Abuse to Political Terror. New York, New York. Basic Books.
Levine, Peter A. (2010). In An Unspoken Voice: How the Body Releases Trauma and Restores Goodness. Berkeley, California. North Atlantic Books.
Levine, Peter A. (2015). Trauma and Memory: Brain and Body in a Search for the Living Past, A Practical Guide for Understanding and Working with Traumatic Memory. North Atlantic Books.
Linklater, Renee. (2014). Decolonizing Trauma Work: Indigenous Stories and Strategies. Blackpoint, Nova Scotia. Fernwood Publishing.
Mate, Gabor. (2003). When the Body Says No: Exploring the Stress-Disease Connection. Nashville, Tennessee. Turner Publishing Company.
Menakem, Resmaa. (2017). My Grandmother’s Hands: Racialized Trauma and the Pathway to Mending Our Hearts and Bodies. Las Vegas, Nevada. Central Recovery Press.
Porges, Stephen W. (2017). The Pocket Guide to the Polyvagal Theory: The Transformative Power of Feeling Safe. New York, New York. W. W. Norton and Company.
Spring, Carolyn. (2019). Unashamed: Healing Trauma-Based Shame through Psychotherapy. 3 Archers Court, Huntingdon, UK: Carolyn Spring Publishing.
Steele, Kathy, Onno van der Hart, and Suzette Boon. (2011). Coping with Trauma-Related Dissociation: Skills Training for Patients and Therapists. New York, New York. W. W. Norton and Company.
Treleaven, David A. (2018). Trauma Sensitive Mindfulness: Practices for Safe and Transformative Healing. New York, New York. W. W. Norton and Company.
Van Der Kolk, Bessel. (2014). The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind and Body in the Healing of Trauma. New York, New York. Penguin Books.
Van Marter Souers, Kristin, and Pete Hall. (2018) Relationship, Responsibility and Regulation: Trauma-invested Practices for Fostering Resilient Learners. Alexandria, VA. ASCD.
Walker, Pete. (2013). Complex PTSD: From Surviving to Thriving. An Azure Coyote Book.
Wiley, Meredith S., and Robin Karr-Morse. (2012). Scared Sick: The Role of Childhood Trauma in Adult Disease. New York, New York. Basic Books.
Header Photo: Dan Meyers, Unsplash