Author’s Note: This post is a fluid and organic piece of writing, and I want to be transparent about that. As people ask questions or call out issues with language, lack of clarity, and other problems, I am working to make changes and keep shaping this piece. I’m open to discussing any of these changes, as well. I also want to acknowledge that this piece may be largely intended for a white audience, although I don’t think it’s limited in that way.
Written by Mike Murawski
As I sit down to write this post, I find myself reflecting on the sometimes frustratingly slow, pain-laden, and capricious path of change for museums, and my own role as an agent of change and accomplice in this work of making change happen. I’ve got a towering pile of books on the shelf in front of me on museum change, activism, and inclusive practices along with a formidable pile of diversity statements and strategic plans that talk about equity and community. Conference after conference and convening after convening bring to the center themes of equity, inclusion, relevance, community, and audience. There are rapidly growing networks of activists and changemakers, with expanding movements connecting through social actions, events, book clubs, reading lists, online syllabi, and social media hashtags. Yet given all this, why do some of the pivotal changes happening in museums right now feel tenuous and temporary? Why does deep and meaningful change feel a bit out of reach?
In a recent piece by poet, activist, and community organizer Jamara Wakefield that powerfully envisions a decolonized future for museums, she writes:
“Museums could be one of our greatest allies in liberation struggles. They have the physical space, the means, and the public confidence to partake in a large scale social movement against colonial powers. Yet they reject this opportunity over and over again. They prefer to remain silent and hide in a world that desperately needs decolonizing.”
One of the things holding us museums back from this level of transformative change is our continued unwillingness to challenge the entrenched institutional structures that advance and maintain inequity. The pervasive hold of white supremacy is arguably one of the single greatest threats to the deep, transformational change that is needed within museums today. It is a threat to racial equity; it is a threat to environmental and economic justice; it is a threat to the well-being of communities of color; it is a threat to human dignity; and it is a threat to those who are struggling to see these universal values of equity, justice, and dignity define our new institutional realities. And it is a threat that is largely-unacknowledged by white museum professionals and leaders across the field.
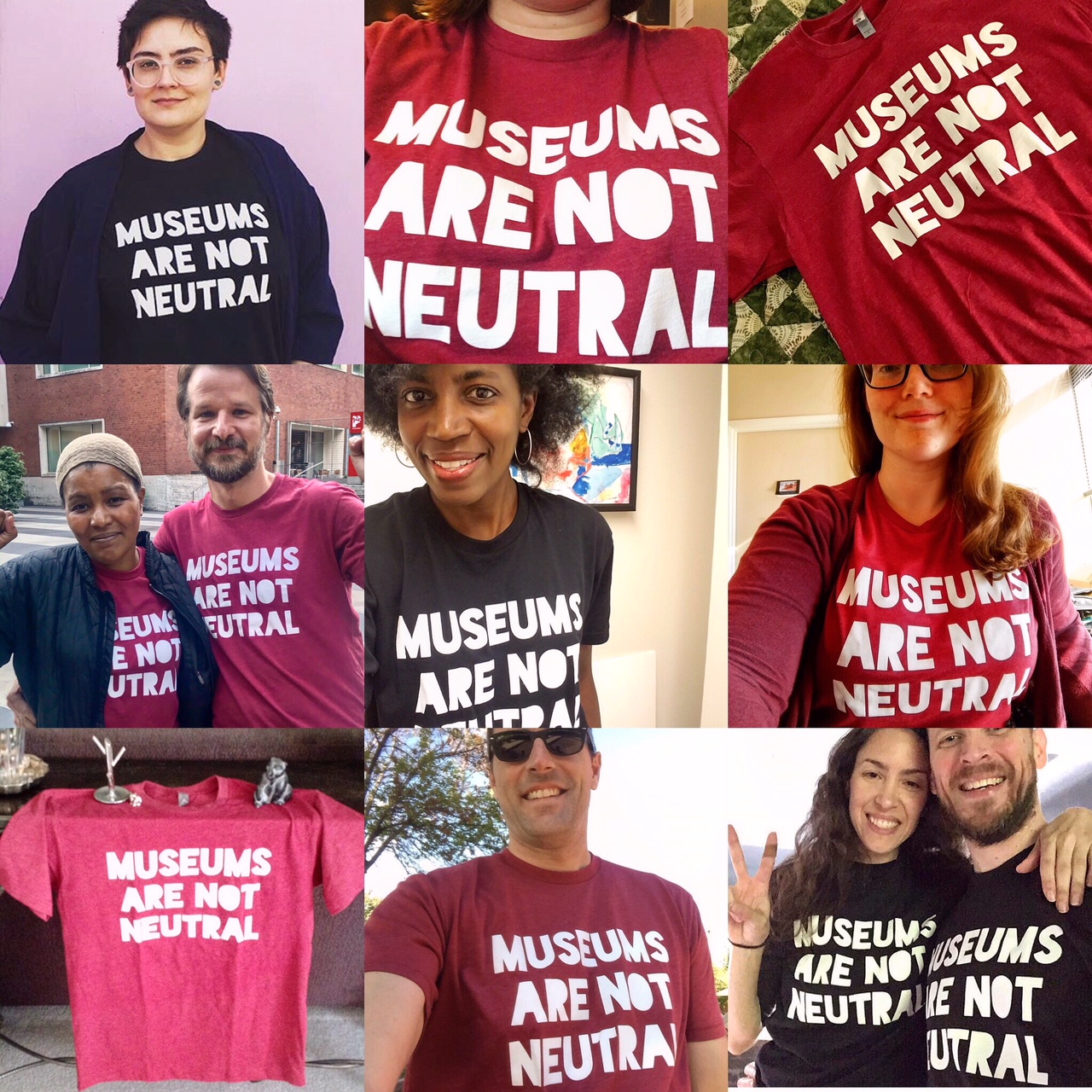

I realize that pressing this idea of examining white supremacy and white dominant culture within our museum institutions may bring forward some resistance, defensiveness, tension, and complexity. During the past two years of spreading the #MuseumsAreNotNeutral campaign and message with co-creator La Tanya Autry, we have encountered resistance (sometimes staunch, sometimes more subtle) from some museum leaders and thinkers (all white) who are unable or unwilling to see, define, and critically reflect on white dominant culture in their institutions. After all, for me, that campaign is so much about the simple yet powerful recognition that what museums take for granted as ‘neutral,’ ‘objective,’ ‘normal,’ ‘professional,’ and ‘high quality’ is all part of a system of white supremacy that perpetuates oppression, racism, injustice, and colonialism.
In an interview this past week, incoming Secretary of the Smithsonian Lonnie Bunch was asked about what #MuseumsAreNotNeutral means to him. He replied:
“It’s crucially important for museums to open the veil, of how they do the work they do so that even they understand the complicit biases they carry. They understand the cultural baggage that shapes what we do.”
I frequently reference the words of scholar and activist Angela Davis who, while speaking to a gathering of Ferguson protesters in 2015, stated:
“Any critical engagement with racism requires us to understand the tyranny of the universal. For most of our history the very category ‘human’ has not embraced Black people and people of color. Its abstractness has been colored white and gendered male.”
White supremacy thrives within this tyranny of the universal, the neutral, the apolitical, the fair and balanced, and the objective. Acknowledging that ‘museums are not neutral’ is a meaningful and urgent step toward gaining awareness of the powerful role that white supremacy and white dominant culture play within our institutions. It is a crucial step toward recognizing one’s own role in questioning it, interrupting it, and being a part of taking transformative action to replace it.
How can we define white dominant culture and white supremacy?
As part of this discussion, I want to bring in a couple definitions of white dominant culture and white supremacy that can be helpful for those who are new to these ideas. If you hear these terms and limit their definitions to the acts of militant white nationalists and hate groups marching with torches, then I suggest you pause here and do some homework. Take some time to connect with the wider discourse around this topic. It is important that we get past these reductive associations, and begin to develop more complex and shared understandings. Robin DiAngelo, author of White Fragility (2018), firmly states the importance of using language such as white dominance and white supremacy in these conversations. She writes:
“White supremacy describes the culture we live in, a culture that positions white people and all that is associated with them (whiteness) as ideal. White supremacy is more than the idea that whites are superior to people of color; it is the deeper premise that supports this idea—the definition of whites as the norm or standard for human, and people of color as a deviation from that norm.” (33)
A useful and widely-recognized definition of white dominant culture comes from the work of Tema Okun and Kenneth Jones on dismantling racism:
“The explicit to subtle ways that the norms, preferences, and fears of white European descended people overwhelmingly shape how we organize our work and institutions, see ourselves and others, interact with one another and with time, and make decisions.”
From their collection of writings entitled How We Fight White Supremacy (2019), Akiba Solomon and Kenrya Rankin write:
“White supremacy defines our current reality. It is not merely a belief that to be White is to be better. It is a political, cultural, and economic system premised on the subjugation of people who are not White…. White supremacy is the voice in our collective heads that says it makes civilized sense that one group of people gets to annihilate, enslave, incarcerate, brainwash, torture, sterilize, breed, and terrorize other people.” (vii)

Through their work on racism, Okun and Jones have also offered up a list of characteristics of white culture that can help us see where white dominant culture is showing up in our work and in our lives on a regular basis. These include perfectionism, a sense of urgency, defensiveness, either/or thinking, a focus on quantity and valuing measurable goals, discomfort with emotion, a sense of paternalism in decision making, and fear of conflict, just to name a few.
For some of you reading this, these characteristics may be strikingly familiar and precisely describe your workplace culture. Have you taken a moment to step back and question some of these norms? How have you been involved in promoting and advancing this culture? I can say that I have spent much of my career in management roles without actively questioning and interrupting these characteristics, playing my own role in maintaining these structures of inequity without being conscious of the impact. My goal here is not to make this about blame or guilt (that happens far too often), but rather to invite white folks to recognize where this is showing up so we can work as part of a collective effort to interrupt and decenter it.
Aspects of white supremacy are showing up every moment of every day in the museum workplace (and in the galleries). It dictates how people hold meetings together, who is invited to those meetings, who participates, and whose ideas are valued. It informs how students of color are treated during a field trip, and how a museum responds when instances of racism hit the media. It controls how our front of house staff interact with visitors, who works in positions that interact with visitors, the types of training they receive, and who makes decisions about these trainings. It dictates how museum leaders and managers make decisions, who gets to have input into those decisions, and who is impacted by those decisions. It is a controlling force in how we define ‘community,’ how we work with community partners, what we value about those partnerships, and how we resource those partnerships. It dictates the words that get written on museum labels, and who gets to write, edit, and approve those words. And each and every one of these moments (and thousands more) threatens to chip away at the humanity of our colleagues of color, visitors of color, and all those who are not defined within these norms of ‘whiteness.’
Real harm is being done throughout every nook and cranny of our institutions, and we need to collectively recognize this before we can take actions to interrupt white dominance. As Gita Gulati-Partee and Maggie Potapchuk state in their 2014 article on “Paying Attention to White Culture and Privilege”:
“not doing this examination means that any equity conversations and work will continue to take place in a larger container that is shaped by the very dynamics that the group aims to change.” (27)
Why am I writing about this?
I want to be clear here. I understand that I am a product of white dominant culture and a participant in white dominant culture, not just as a white, heterosexual, cisgender, able-bodied male in a position of power within a museum, but as a human being living and acting in our society. White supremacy is insidious, pervasive, and systemic. It is the air we breathe. It shapes our language, our relationships, our actions, our decisions, and our emotions. It is showing up in my words as I write this, even as I critique it. And while I have made choices to gain awareness of this domineering and harmful culture, it still floods all aspects of my being in this world.
I have chosen to make my messy and mistake-filled learning process more public, not to create harm but rather to recognize these challenges wherever, whenever, and however possible. Throughout my museum career, I have leaned towards questioning the status quo and the “ways things are supposed to be” without necessarily having ‘the answer.’ I enjoy the more fluid exchange of ideas, questions, and experiences that we, as a broader collective of changemakers, can bring to these issues. I find that it is important to open up larger and larger conversations about burning issues so that we can grow together as a community of change and work toward building a positive, thriving future for museums.
I raise these questions about white supremacy as part of a rapidly expanding group of museum workers, leaders, and advocates for change who see the language of diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility spread like wildfire on the surface of museums without necessarily seeing the deep institutional transformations that are needed within museums. I also raise these questions as someone working within a museum that is changing and experiencing the pain and messiness of grappling with these deeper issues. My own learning has been happening over the course of many years in conversation and allyship with colleagues, mentors, friends, co-workers, and the many teachers in my life. I also recognize the long history of museum workers, activists, educators, community leaders, and radical transformers who have fought against white supremacy, and those who I see as powerful leaders and mentors in current efforts to dismantle racism and change museums (including La Tanya Autry, Monica Montgomery, Teressa Raiford, Keonna Hendrick, Porchia Moore, Radiah Harper, Nicole Ivy, Omar Eaton-Martinez, Chris Taylor, Janeen Bryant, nikhil trivedi, Jackie Peterson, Melanie Adams, Joanne Rizzi-Jones, Dina Bailey, PJ Gubatina Policarpio, Stephanie Cunningham, Aleia Brown, Adrianne Russell, Kayleigh Bryant Greenwell, Chieko Phillips, Elisabeth Callihan, Laura Raicovich, Aletheia Wittman, Alyssa Greenberg, Margaret Middleton, Toni Wynn, those working on MASS Action, the Museums and Race team, and many many others). I am aware of, and grateful for, the deep thinking and action that has already been done around this issue, and that continues to be done today.
Taking action to interrupt white supremacy
The work of interrupting and decentering white supremacy can seem overwhelmingly daunting when we’re faced with what seems like the insurmountable task of systemic change. Furthermore, there is no easy fix, mandatory training, or simple pre-packaged strategy that can wash away these oppressive structures and legacies. As Solomon and Rankin aptly state, “if we had a magic button we could press to end this nightmare, we would have leaned on that bitch long ago” (x).
One important place to start, especially for white people, is to simply recognize and name when white culture is showing up in the workplace — and accept the discomfort that comes with identifying these moments without resorting to defensiveness (see “white fragility”). In a widely-shared blog post on challenging white dominant culture in nonprofits, Lupe Poblano, Project Director at CompassPoint, writes, “White leaders … need to locate their own cultural whiteness and become aware of how their internalized superiority shows up and how it negatively impacts POC inside their own organization.” He continues, “You, leaders within the white dominant leadership structure, need to be willing to change you first.”
Gulati-Partee and Potapchuk stress that “putting white culture and privilege on the table is critical to include in racial equity work—and it is fraught with challenges due to the complex manifestations of structural racism.” For those doing the more transformational work in museums, I know that you feel these challenges each and every day. For most white people, myself included, the larger structures of white supremacy are elusive and invisible until we gain the awareness to see them. And when we do see them more clearly, it feels like a punch in the gut. As Hannah Heller writes in her 2018 article “Working Towards White Allyship in Museums”:
“those moments that feel uncomfortable or anxious are exactly the moments to lean in to as an ally. That feeling is your Whiteness being tested and questioned. Start paying attention to the moments that make you pause….”
Recognizing these characteristics of white dominant culture is a pretty big step for many of us, yet it doesn’t end there. Transformative change begins to happen in our institutional cultures when we examine, interrupt, decenter, and replace these harmful and oppressive organizing structures and habits of mind. Okun and Jones offer an entire set of “antidotes” or alternatives that we can pivot to, moving away from the established norms of white workplace culture. The Museums as Sites of Social Action (MASS Action) toolkit also provides an extremely useful discussion of dominant culture, organizational culture, and inclusion in Chapter 3 and many other sections of the toolkit.
 I also highly recommend that folks check out the BlackSpace Manifesto, created by a collective of Black artists, architects, designers, urbanists, and changemakers working to amplify Black agency. Their Manifesto provides a powerful set of practices that turn us away from white supremacy and center new modes of thinking and working based in equity, justice, love, and trust. I recently shared the Manifesto with a few white colleagues at my own institution, and we met to discuss our own roles in pivoting toward these practices. While it was just one conversation, it’s a small step toward doing things differently.
I also highly recommend that folks check out the BlackSpace Manifesto, created by a collective of Black artists, architects, designers, urbanists, and changemakers working to amplify Black agency. Their Manifesto provides a powerful set of practices that turn us away from white supremacy and center new modes of thinking and working based in equity, justice, love, and trust. I recently shared the Manifesto with a few white colleagues at my own institution, and we met to discuss our own roles in pivoting toward these practices. While it was just one conversation, it’s a small step toward doing things differently.
Download BlackSpaceManifesto (PDF)
After taking time to reflect with colleagues about how we might change workplace culture, I began working on a quick resource (below) that could be front and center on our desks and in our minds. At our museum, we have an existing set of Agreements in place that support our broader equity work, including things like “stay engaged,” “listen to understand,” and “be willing to do things differently.” For about the past year, many staff have inserted the Agreements into their staff ID badge holders as a daily reminder to show up differently in our work.
Along these lines, I am interested in any way we can bring a more regular, daily awareness to white dominant culture and the ways we can collectively work to interrupt and decenter it. Please feel free to download, share, or print the Interrupt White Dominant Culture guide below, and use it to spark conversation and change within your organization or workplace. Or simply use it yourself as a personal reminder to shift your focus and energy away from white supremacy. It’s just an imperfect start to getting these conversations to happen more frequently in museums. And the language and characteristics used in this guide come from the sources I have cited in this post along with much of the research and writing on white dominant culture.

Download InterruptWhiteDominantCulture (PDF)
[TEXT OF INTERRUPT WHITE DOMINANT CULTURE GUIDE]
INTERRUPT WHITE DOMINANT CULTURE
- Let’s work COLLECTIVELY to identify these and other elements of white dominant culture, and work toward dismantling racism in our organizations in in our lives.
- Move from a focus on professional and transactional relationships toward relationships based on trust, care, and shared commitments.
- Move from protecting power to sharing power.
- Move from a culture of over-working to a culture of self-care and community care.
- Move from a competition and struggle for limited resources to a mindset of collaboration and working to share resources.
- Move away from prioritizing only degrees, work experience, and job titles toward a way of recognizing and centering lived experience
- Move from a place of those with power making decisions for others toward a place where we work to include those affected by decisions in the decision-making process.
Speak Up. Take Action.
(recognizing the thinking and writings of Tema Okun, Kenneth Jones, Maggie Potapchuk, BlackSpace Manifesto, Radiah Harper, Hannah Heller, and Kai Monet)
Questioning the ways we make change happen
For me, the spark for writing this piece and creating the guide above came when I was invited to speak at the MuseumNext conference in London (June 2019). The conference’s central theme was “Making Change Happen,” a topic I am extremely passionate about. I spent some time reflecting on the barriers we, as museum professionals and changemakers, face within institutions to make change happen, and how quickly (or slowly) we enact change. For my presentation, I facilitated a bit of a workshop that created some space for conference attendees to think about the larger issues of dominant culture and white supremacy in their own personal work and within our institutions.
I ended with a “Questions & Listening” session, rather than a typical “Question and Answer” thing — which is a strategy I’ve experimented with in the past. This simply allows people to ask questions, gives those questions some space to be heard in a deeper way by everyone, and does not pretend that I (as the “presenter”) am in some kind of ‘expert’ position to give the answers. It allows everyone in the room to reflect on the questions, and potentially have their own conversations about their responses. It honors the knowledge in the room, not just in the “expert presenter.” While this is always a bit awkward, since we’ve been trained to want to hear the answers from the single person on stage, I feel it is a worthwhile strategy to disrupt the white dominant culture that shows up in conferences.

I have also embraced a flood of questions racing through my mind before and after my presentation about change: In our own impatience to see urgent and meaningful change take place, are we unintentionally setting up an antagonism between immediate action and deeper reflection? Are we creating an either/or choice between making change happen now and taking time for conversation, listening, and collective understanding? Do we place more value in the bigger, bolder public-facing actions and downplay the more intimate, personal, relationship-based evolution of change happening on a smaller scale? How much of our mindset about change, and the pace of change, is dictated by white dominant culture?
I am open to your thoughts, insights, questions, and critiques as part of this broader conversation. I intend to remain open-hearted in this work, recognizing that I have a lot of learning ahead of me and a lot of listening to do. I’m committed to being a catalyst for these challenging conversations since I believe in the future of museums and I know in my heart that we collectively have the courage to change these institutions in deep, transformative ways.
“Museums could be powerful, liberatory spaces…”
I’m going to put an exclamation point on the end here by reconnecting with the incredible words of Jamara Wakefield (enormous gratitude to my friend Monica Montgomery for sharing this piece, which I have read about a dozen times in the last couple days). In the article “Museums could be powerful, liberatory spaces if they let go of their colonial practices,” Wakefield concludes with this:
“For my activist, artist, dreamer friends, and all who believe in another world, the one where our lives matter, our histories matter, our liberation matters: be prepared to fight in this world but never stop imagining liberation for our future selves. We owe this moment to our future selves.”
* * *
About the Author
 MIKE MURAWSKI: Changemaker, museum thinker, author, and nature lover living in Portland, Oregon, USA. Mike currently serves as the Director of Learning & Community Partnerships for the Portland Art Museum, and is the founding editor of ArtMuseumTeaching. He earned his MA and PhD in Education from American University in Washington, DC, focusing his research on educational theory and interdisciplinary learning. Prior to his position at the Portland Art Museum, he served as Director of School Services at the Saint Louis Art Museum as well as Coordinator of Education and Public Programs at the Mildred Lane Kemper Art Museum at Washington University in St. Louis. He is a contributor to the Museums as Sites of Social Action (MASS Action) initiative supporting equity and inclusion in museums, and served as First Wave Project Advisor for OF/BY/FOR ALL initiative based out of the Santa Cruz Museum of Art and History helping civic and cultural organizations grow of, by, and for their communities. Mike is proud to be the co-founder of the #MuseumsAreNotNeutral campaign aimed at erasing the myth of museum neutrality and demanding our institutions act as agents of change. He has spoken nationally and internationally on the social responsibilities of museums and how museums can serve as agents of positive change within their own communities. Mike has also been invited to lead participatory workshops, lectures, panels, and training sessions at various institutions, including the Aspen Art Museum, Crocker Art Museum, the Museum of Contemporary Art in San Diego, Los Angeles County Museum of Art, National Gallery of Art, Nelson Atkins Museum of Art, Philadelphia Museum of Art, and Phoenix Art Museum, among others. He is passionate about how we can come to see museums as agents of change in their communities as well as creative sites for transformative learning and social action.
MIKE MURAWSKI: Changemaker, museum thinker, author, and nature lover living in Portland, Oregon, USA. Mike currently serves as the Director of Learning & Community Partnerships for the Portland Art Museum, and is the founding editor of ArtMuseumTeaching. He earned his MA and PhD in Education from American University in Washington, DC, focusing his research on educational theory and interdisciplinary learning. Prior to his position at the Portland Art Museum, he served as Director of School Services at the Saint Louis Art Museum as well as Coordinator of Education and Public Programs at the Mildred Lane Kemper Art Museum at Washington University in St. Louis. He is a contributor to the Museums as Sites of Social Action (MASS Action) initiative supporting equity and inclusion in museums, and served as First Wave Project Advisor for OF/BY/FOR ALL initiative based out of the Santa Cruz Museum of Art and History helping civic and cultural organizations grow of, by, and for their communities. Mike is proud to be the co-founder of the #MuseumsAreNotNeutral campaign aimed at erasing the myth of museum neutrality and demanding our institutions act as agents of change. He has spoken nationally and internationally on the social responsibilities of museums and how museums can serve as agents of positive change within their own communities. Mike has also been invited to lead participatory workshops, lectures, panels, and training sessions at various institutions, including the Aspen Art Museum, Crocker Art Museum, the Museum of Contemporary Art in San Diego, Los Angeles County Museum of Art, National Gallery of Art, Nelson Atkins Museum of Art, Philadelphia Museum of Art, and Phoenix Art Museum, among others. He is passionate about how we can come to see museums as agents of change in their communities as well as creative sites for transformative learning and social action.
Mike’s postings on this site are his own and don’t represent the Portland Art Museum’s positions, strategies, or opinions.












 I also highly recommend that folks check out the
I also highly recommend that folks check out the 

 MIKE MURAWSKI: Changemaker, museum thinker, author, and nature lover living in Portland, Oregon, USA. Mike currently serves as the Director of Learning & Community Partnerships for the Portland Art Museum, and is the founding editor of ArtMuseumTeaching. He earned his MA and PhD in Education from American University in Washington, DC, focusing his research on educational theory and interdisciplinary learning. Prior to his position at the Portland Art Museum, he served as Director of School Services at the Saint Louis Art Museum as well as Coordinator of Education and Public Programs at the Mildred Lane Kemper Art Museum at Washington University in St. Louis. He is a contributor to the Museums as Sites of Social Action (MASS Action) initiative supporting equity and inclusion in museums, and served as First Wave Project Advisor for OF/BY/FOR ALL initiative based out of the Santa Cruz Museum of Art and History helping civic and cultural organizations grow of, by, and for their communities. Mike is proud to be the co-founder of the #MuseumsAreNotNeutral campaign aimed at erasing the myth of museum neutrality and demanding our institutions act as agents of change. He has spoken nationally and internationally on the social responsibilities of museums and how museums can serve as agents of positive change within their own communities. Mike has also been invited to lead participatory workshops, lectures, panels, and training sessions at various institutions, including the
MIKE MURAWSKI: Changemaker, museum thinker, author, and nature lover living in Portland, Oregon, USA. Mike currently serves as the Director of Learning & Community Partnerships for the Portland Art Museum, and is the founding editor of ArtMuseumTeaching. He earned his MA and PhD in Education from American University in Washington, DC, focusing his research on educational theory and interdisciplinary learning. Prior to his position at the Portland Art Museum, he served as Director of School Services at the Saint Louis Art Museum as well as Coordinator of Education and Public Programs at the Mildred Lane Kemper Art Museum at Washington University in St. Louis. He is a contributor to the Museums as Sites of Social Action (MASS Action) initiative supporting equity and inclusion in museums, and served as First Wave Project Advisor for OF/BY/FOR ALL initiative based out of the Santa Cruz Museum of Art and History helping civic and cultural organizations grow of, by, and for their communities. Mike is proud to be the co-founder of the #MuseumsAreNotNeutral campaign aimed at erasing the myth of museum neutrality and demanding our institutions act as agents of change. He has spoken nationally and internationally on the social responsibilities of museums and how museums can serve as agents of positive change within their own communities. Mike has also been invited to lead participatory workshops, lectures, panels, and training sessions at various institutions, including the 

 MIKE MURAWSKI: Founding author and editor of ArtMuseumTeaching.com, museum educator, and currently the Director of Education & Public Programs for the
MIKE MURAWSKI: Founding author and editor of ArtMuseumTeaching.com, museum educator, and currently the Director of Education & Public Programs for the